Currencies are the lifeblood of the global economy, differentially flowing at various speeds across the arteries of international trade. With these dynamic flows, th Forex market has become one of the popular avenues for traders aiming to profit from sizable currency fluctuations. With 2024 on the horizon, a seismic shift in Forex trading strategies is anticipated, driven by rapidly changing geopolitical landscapes, evolving economic scenarios, and the continuous quest for higher profitability.
In this article, we aim to unravel some of the most promising Forex trading strategies tailored for 2024, providing traders a roadmap to navigate through the ebbs and flows of global currency markets. From scalping to swing trading, let's explore which strategies offer abundant opportunities in 2024.
What is a Forex Trading Strategy?
A Forex trading strategy is a technique used by a Forex trader to determine whether to buy or sell a currency pair at any given time. These strategies can be based on technical analysis, chart analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of them. Forex trading strategies are developed to cater to different trading styles, risk tolerance, and goals.
Examples of these strategies include the Trend Trading Strategy, Price Action Trading Strategy, Scalping, Swing Trading, and Position Trading, among others. The objective of a Forex strategy is to create trade signals that a trader can use to time their trades and profit from currency price movements.
What are the Best Forex Trading Strategies?
① Forex Scalping Strategy
This is a short-term strategy that involves making a large number of trades with the aim of making small profits from each. It requires a strict exit strategy as a large loss could eliminate the many small gains achieved.
| Length of Trade | Very short, typically minutes. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Multiple trades a day to capitalize on small price movements; entry and exit points are usually decided by minor price fluctuations or certain technical setups. |
Time Frames: Scalping usually occurs on shorter time frames like the 1-minute or 5-minute charts. Some scalpers may also use slightly longer time frames like the 15-minute or 30-minute charts.
Trade Frequency: Scalpers make numerous trades in a day. Depending on market conditions, this could range from dozens to hundreds of trades.
Small Profit Targets: The goal is typically to capture a few pips per trade. Scalpers could set profit targets of around 5-10 pips per trade, depending on the pair and current market volatility.
Technical Analysis: Scalping heavily relies on technical analysis and price action. Indicators, such as moving averages, stochastic oscillators, and Bollinger Bands, can often be used to identify entry and exit points. Additionally, support and resistance levels are often closely watched.
Trading Software: Due to the quick-paced nature of scalping, efficient and reliable trading software is important. Some scalpers might also use trading software with automation capabilities.
Preferable Market Conditions: Scalpers often prefer a stable market and would avoid trading in choppy or highly volatile conditions.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Can yield consistent small profits. | × Requires a significant amount of time and attention. |
| √ Less exposure to the market as positions are opened and closed quickly. | × High transaction costs due to the large number of trades. |
| √ Less likely to be affected by large market moves. | × May lead to large losses if not managed appropriately. |
Example:
Consider a forex pair in a strong upward or downward trend. Use two Moving Averages (like 50 and 200-day moving averages), and wait for the lower period MA to cross over the higher period MA, indicating a trend. Once this cross happens, enter a trade in the direction of the trend and aim for around 5-10 pips profit.
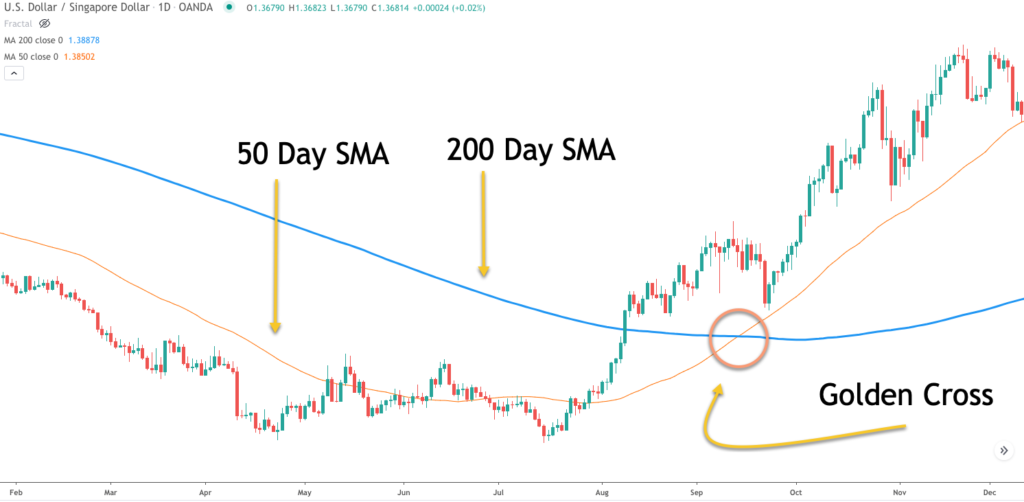
⚠ Scalping requires quick decision-making skills and swift execution.
② Position Trading Strategy
Position trading is a longer-term strategy that might involve holding a position for months to years. Traders utilizing this strategy primarily rely on fundamental analysis, and would use technical analysis mainly to better time their entries and exits.
| Length of Trade | Long-term, from months to years. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Based on more extensive macroeconomic fundamentals; entry is usually during periods of price retracement within a trend and exit when the fundamental analysis shows a possible trend reversal. |
Fundamental Analysis: The primary analysis method. Traders use macroeconomic data, company/industry prospects, monetary policy, and various other factors to evaluate the overall health of a currency pair's respective economies.
Technical Analysis: This is used in conjunction with fundamental analysis. Traders use it primarily to determine the best entry or exit points and to confirm or reject the signals from the fundamental analysis.
Patience: Since trades are held open for a long period of time, patience is a virtue. It can take a while for the market to move in the desired direction.
Market Trends: Position traders typically take a directional bias. They want to take trades in the direction of the overall trend, as the longer-term trends can provide more profit potential.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Requires less time as trades are done over a longer period. | × Requires a deep understanding of fundamental analysis. |
| √ Less stress and fewer decisions to make. | × Longer holding periods may result in bigger losses if the market moves against you. |
| √ Allows for large profits if the market significantly moves in your favor. | × Generally requires a larger capital outlay. |
Example:
Suppose a position trader conducts a fundamental analysis and concludes that the US economy will be stronger than the Japanese economy. They would consider going long on USD/JPY. They might look at the weekly or monthly chart to identify the overall trend and find a suitable entry point. Maybe they'll use a moving average or trendline to identify the trend. After entering the trade, they would set a stop loss at a level that represents a tolerable risk for them.

⚠ Position trading requires in-depth knowledge and understanding of markets and fundamental catalysts. This is due to the long-term nature of trades and the possibility of being affected by different events and changes in market conditions through holding periods.
③ Trend Trading/Following Strategy
Trend trading, also known as trend following, is a strategy utilized by traders who aim to capitalize on upward or downward price trends in a market. It is a longer-term strategy where traders analyze and identify possible trends, and position their trades in the direction of the trend.
| Length of Trade | Medium to long-term, weeks to months. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Enters a trade when signs of a trend are confirmed and exits when there are indications of the trend ending or reversing. |
Identify the Trend: The first step in trend trading is identifying the trend. This can be done using technical analysis tools like moving averages, trendlines, or technical indicators like the MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence) or ADX (Average Directional Index).
Entry Point: Once the trend is identified, the next step is determining an optimal entry point. This might involve waiting for a pullback or retracement within the overall trend, or using technical signals like a moving average crossover.
Stacking Positions: Some trend traders choose to “stack” their positions. As the trend continues, they add additional positions, attempting to maximize their profits from the trend.
Stop Loss and Take Profit Levels: Given the longer-term nature of trend trading, traders often use wider stop loss and take profit levels. The aim is to stay in the trend as long as it lasts, and avoid being stopped out by temporary price fluctuations.
Exit Strategy: Eventually, the trend will meet its end. Many trend traders use technical signals to exit their trades. For example, they may choose to exit when the price closes below a moving average in an uptrend, signaling a potential trend reversal.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Potential for substantial profits in major trends. | × Requires patient and discipline as trades may take time to develop. |
| √ Gives a clear trading direction. | × False signals can lead to losses. |
| √ Allows for some losses as long as the overall trend remains profitable. | × Dependence on identifying the correct trend direction. |
Example:
Imagine you're trading the GBP/USD currency pair. From your observation, you discern that a substantial downtrend is in effect. To confirm this, you apply a 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). The EMA is steadily declining, and the GBP/USD price remains below this EMA, further supporting your analysis. Given the trend, you make the decision to go short.
You consider that an appropriate entry point would be during a mild increase in price, aligning with a resistance level. You set your stop loss above the previous swing high to ensure protection should the trend reverse. As for your exit strategy, you plan to close your position if the price ascends above the 200-day EMA, signifying that the downtrend could be concluding.
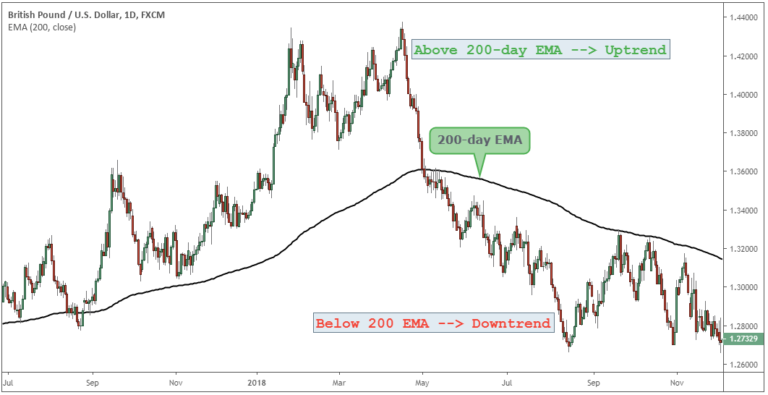
④ Price Action Trading Strategy
Price action trading is a strategy that relies on the raw price data of a market to make trading decisions. Instead of relying on technical indicators or other mathematical models, the focus shifts to actual price movements.
| Length of Trade | Depending on the trader; can be minutes for day traders and weeks for swing or position traders. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Trades are entered based on price patterns or setups, and exits are generally set in relation to support or resistance levels or other price pattern detections. |
Understand Candlestick Patterns: One of the foundational aspects of price action trading is understanding candlestick patterns. This includes individual candles and groups of candles (known as candlestick patterns) that form specific shapes or designs. For example, traders might look for doji, pin bar, or engulfing patterns.
Identify Support and Resistance Levels: In price action trading, much attention is given to identifying key levels of support and resistance. These levels act as barriers that prevent the price from moving higher or lower.
Trend Lines and Channels: These are lines drawn on the price chart that help identify the direction of market trends. They help traders visually see the trend and provide areas of support and resistance.
Price Breakouts: This happens when the price moves above a resistance level or below a support level. Breakouts can be substantial and swift, so many traders watch for these occurrences.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Flexibility as it can be used in different markets and timeframes. | × Can be subjective and open to interpretation. |
| √ Focuses on raw data, removing the need for lagging indicators. | × Requires in-depth knowledge and experience to be effective. |
| √ Can be simpler as there are no complex formulas or algorithms. | × Understanding different candlestick patterns and trends can be complex. |
Example:
Suppose you're watching the EUR/USD. The pair forms a bullish engulfing pattern at a notable support level, suggesting a potential reversal or bounce back to the upside. You decide to enter a long position after the close of the engulfing candle, placing your stop loss beneath the support level.
For your exit strategy, you plan to aim for a previous resistance level and also watch for any reversal candlestick patterns or behavior indicating the price may reverse again.
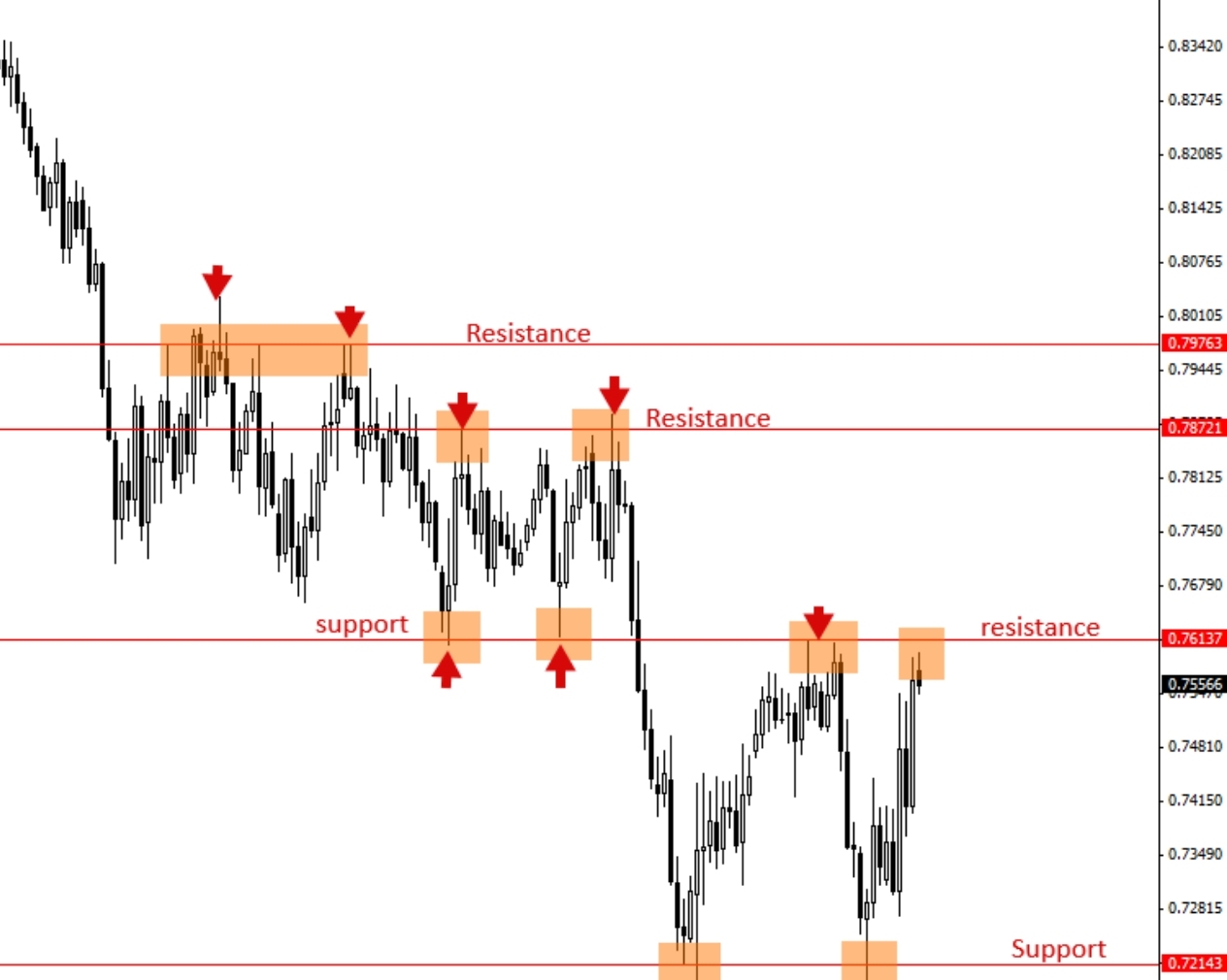
⑤ Range Trading Strategy
Range trading, also known as sideways trading or channel trading, is a strategy utilized when a currency or asset experiences little in terms of upward or downward movement. The price tends to oscillate between the high and low levels, known as the resistance and support levels, respectively. In this state, it is said to be moving in a 'range'.
| Length of Trade | Short to medium-term, typically days to weeks. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Entries are often made at the observed support level of the range, and exit points at the observed resistance level. |
Identify the Range: The first step is to identify a range bound market. This can be done using technical analysis to spot horizontal support and resistance levels between which the price is oscillating over a period.
Entry Point: Once a range is identified, a trader would typically buy at or near the identified support level (range low), and sell at or near the identified resistance level (range high).
Technical Indicators: Traders often use technical indicators such as the RSI (Relative Strength Index), stochastic oscillator or Bollinger Bands® to help identify overbought and oversold conditions. These conditions often occur at the range highs and lows, providing extra confirmation for range traders.
Stop-Loss Orders: Ideally, a stop-loss should be put just outside the range to protect against potential breakouts. For example, if you are buying at the support level, you would place your stop just below the range.
Take-Profit Orders: These are typically placed just before the opposing level of support or resistance. Traders will aim to take profit just before the price reaches these levels, since it is where the price is likely to reverse.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Effective in markets with no clear direction. | × False breakouts can lead to losses. |
| √ Clear entry and exit points. | × Not effective in strong trending markets. |
| √ Lower risk compared to trending strategies if the range holds. | × May require constant market monitoring. |
Example:
Let's consider youre looking at the GBP/USD forex pair. After analysis, you find that it's in a range-bound state, bouncing between a resistance level at 1.3150 and a support level at 1.3000.
In this situation according to the range trading strategy, you might decide to enter a buy order at the support level (1.3000) and a sell order at the resistance level (1.3150). To manage your risk, you might set a stop-loss slightly below the support level for your buy order and slightly above the resistance level for your sell order. Your take-profit orders could be slightly below the resistance level for the buy order, and slightly above the support level for the sell order.
⑥ Swing Trading Strategy
This is a medium-term strategy where positions are held for days to weeks. Swing traders aim to capture the “swing” or change in momentum of a currency pair.
| Length of Trade | Typically holding positions for days to weeks. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Swing traders aim to enter a trade at the start of a price movement (swing) and exit once the price movement seems to run out of steam. |
Identifying Trends: The first step is identifying an overall trend in the market whether it's upwards or downwards. This can be achieved using trend indicators or just by observing price action over a period. Once the trend is identified, a swing trader looks for price movements within this trend.
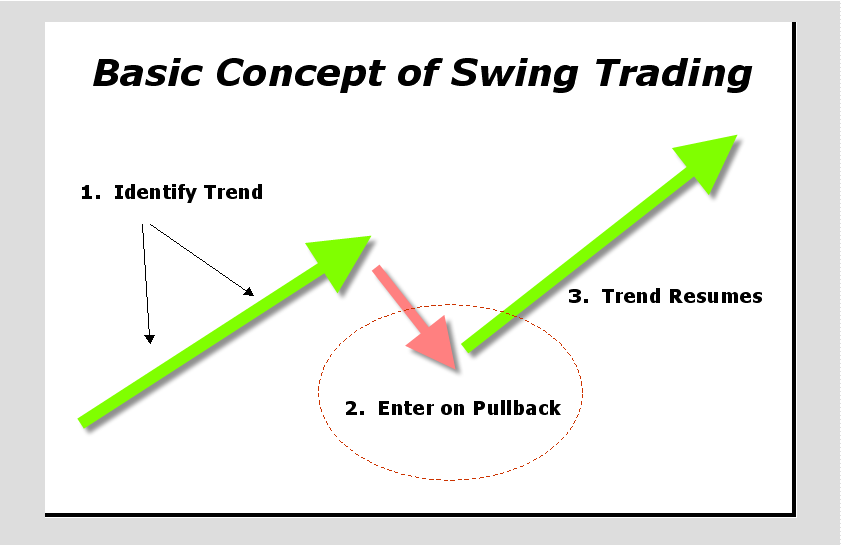
Choosing Entry Points: This can be done by looking for price reversals, retracements, or normal market corrections within an overall trend. Swing traders usually have specific price targets in mind for entry, which are levels where they anticipate the price will change direction and “swing”.
Setting Stop Losses: Swing trading often involves extensive use of stop-loss orders to manage risk. These are typically set at levels where the trader acknowledges their analysis was wrong and would therefore want to exit the trade.
Spotting Overbought or Oversold Conditions: RSI (Relative Strength Index) is one of the most commonly used indicators in swing trading. It helps determine when a market might be overbought or oversold, providing a hint that a reversal may be imminent.
Exit Strategy: The goal of a swing trader is to sell as close to the price peak as possible. Swing traders typically use a combination of risk-reward ratios and pre-set price targets to guide their decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Profitable in volatile markets. | × Requires in-depth knowledge of technical analysis. |
| √ Doesn't require constant monitoring like scalping or day trading. | × Keeping positions open overnight may lead to negative impacts from sudden market changes. |
| √ Allows traders to take advantage of short-term trends. | × Swing traders can miss longer-term trends in favor of short-term gains. |
Example:
Imagine you are following the EUR/USD pair, which is in an overall upward trend. You notice a pullback versus the overall trend, which a swing trader might view as an opportunity to go long before the trend resumes.
You could use the RSI to help identify when the market is oversold within your discovered trend, suggesting that the pullback might be ending soon. After entering the trade, you would set your stop loss below the recent swing low and set your target price near the recent swing high.
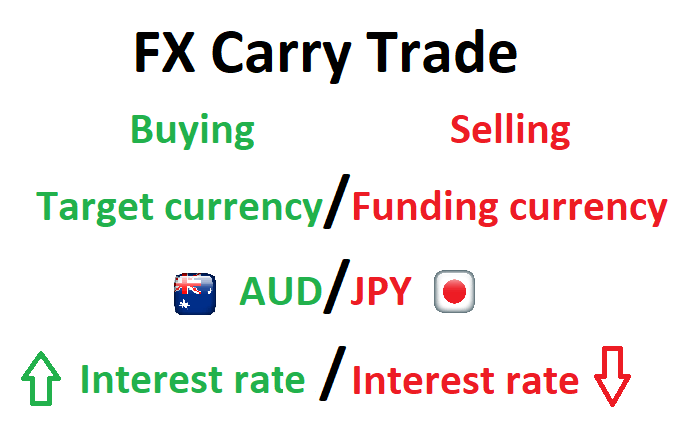
⑦ Carry Trade Strategy (Most Used)
Carry trade is a strategy that involves borrowing at a low interest rate and investing in an asset that provides a higher rate of return. Carry Trade is most often used in the Forex market.
| Length of Trade | Long-term, they can be held for months or even years. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Trades are typically entered when there is a high differential between high and low yield currencies, and are exited when the exchange rate becomes too unfavorable or the differential narrows significantly. |
Identify the Interest Rate Differential: The first step in a carry trade strategy is to identify a currency pair with a large interest rate differential.
Buy/Hold a High Interest Rate Currency: Once the currency pair is identified, the next step is to buy or hold the high interest rate currency and sell or borrow the low interest rate currency. Essentially, you are earning the interest on the currency that you have bought and paying the interest on the currency that you have sold.
Leverage: Typically for the carry trade strategy to be effective and produce more substantial profits, leverage is used. However, its important to remember that while leverage can amplify profits, it can also magnify losses.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Allows traders to profit from interest rate differentials. | × Involves risks such as interest rate fluctuations and changes in currency values. |
| √ Can be profitable and less stressful over the long term. | × Requires a deep understanding of forex markets. |
| × Uncertainty and unpredictability associated with long-term trades. |
Example:
For example, let's say you notice a large interest differential between AUD (Australian Dollar) and JPY (Japanese Yen). You decide to borrow a large sum of JPY because of Japan's low interest rate and then convert that into AUD. Then, you invest that AUD in a bond earning a high return. Assuming the AUD/JPY exchange rate does not change, you would profit from the difference in interest rates - earning interest on AUD and paying interest on JPY.
⑧ Day Trading Strategy
Day trading is a trading style that involves entering and exiting trades within the same trading day. The goal is to capitalize on small movements in the prices of currency pairs or other financial assets.
| Length of Trade | Very short, with all trades closed by the end of the trading day. |
| Entry/Exit Points | Multiple trades occur daily, based on trend patterns, news, and technical cues; entry and exit points need to be precisely timed over the course of the trading day. |
Technical Analysis: Day traders typically rely heavily on technical analysis, looking for patterns in the price charts or using technical indicators that signal trading opportunities.
Market Volatility: Since day trading relies on capturing small price movements, trading during times of high volatility is often beneficial. Many day traders trade during the opening hours of the market, where volatility tends to be highest.
Discipline: Day trading requires discipline and consistency. Day traders need to be able to follow their trading plan and not let emotions like fear or greed dictate their trading decisions.
| Pros | Cons |
| √ Can profit from small intraday market price fluctuations. | × Can be stressful due to the fast pace and need for constant market monitoring. |
| √ No risk of overnight market changes affecting trades. | × High transaction costs due to the number of trades made. |
| × Requires strong discipline, the right tools, and a stable internet connection. |
Example:
For instance, a day trader might use a basic breakout strategy. Breakouts occur when price breaks through an identified level of support or resistance. The trader will put a buy order just above resistance or a sell order just below support in anticipation of the breakout. Placing stop losses just above resistance for sell orders or just below support for buy orders limits potential losses.
⚠ Day trading requires fast decision-making and execution. It also requires a good understanding of trading principles and a very disciplined mind.
Why do You Need a Forex Trading Strategy?
Objective Trading
A well-developed trading strategy includes specific rules for entering and exiting trades. It eliminates subjectivity, impulsive actions, and emotional trading decisions which can often lead to large losses.
Risk Management
A trading strategy helps you define your risk level and stick to it. It aids in determining the ideal position size for each trade according to your risk tolerance, consequently protecting your trading account from being overexposed to risk.
Profitability
By adhering consistently to a strategy that works well for you, you can increase your chances of becoming profitable in the long run. A good strategy helps identify high-probability trade setups.
Consistency
A trading strategy helps you trade consistently. Each defined rule needs to be adhered to for every trade, which brings in a structured and uniform approach to trading.
Performance Measurement and Improvement
Having a predefined strategy allows you to log and measure your performance better. By reviewing your trading history, you can figure out what works, what doesn't, and fine-tune your strategy accordingly to improve performance.
If you don't have a solid trading strategy, you are likely to fall victim to your emotions, leading to erratic trading decisions and potential losses.
How to Choose the Best Forex Trading Strategy?
Trading Goals
Your goals will largely determine the type of strategy you use.
| Trading Goal | Trading Strategy |
| Short-term profits | Day trading/scalping |
| Longer-term investments | Trend trading/position trading |
Risk Tolerance
Different strategies have different levels of risk.
| Risk Tolerance | Trades | Trading Strategy |
| Less | More | Scalping |
| Higher | Fewer | Position trading |
Time Commitment
Consider how much time you're able to dedicate to trading.
| Time Commitment | Trading Strategy |
| A lot of time and attention | Day trading/scalping |
| Less day-to-day management | Position trading/swing trading |
Skill Level
Some strategies are more complex than others and require more experience or knowledge to execute successfully.
| Skill Level | Trading Strategy | Suitable for |
| Simpler | Trend trading | Beginners |
| Complex | Price action trading | More experienced traders |
Market Conditions
Certain strategies perform better under specific market conditions.
| Market Condition | Trading Strategy |
| Sideway | Range trading |
| Directional | Trend trading |
Tips for Beginners
Educate Yourself
Trading Forex isn't something you can just jump into. There are many different aspects to trading that you need to understand before you start, including how to interpret Forex quotes, charts, and trend lines, which trading platform to use, how to place trades, and a multitude of other topics. Online resources, books, and courses can be of great help.
Choose a Reliable Forex Broker
Find a broker that is regulated by a reliable authority. There are a lot of brokers out there, but not all are trustworthy. Make sure to read reviews and carefully check the specifications and offerings of each.
At WikiFX, we've meticulously compiled a variety of ranking lists of best brokers influenced by factors such as geographical location and trading conditions, among others. Follow us for further insights and to deepen your understanding of forex trading.
Implement Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying potential risks in advance, analyzing them, and taking precautionary steps to reduce your risk. Start trading with small lots and use stop-loss orders to limit your risk.
Practice with a Demo Account
Before you start trading on the market, open a demo account with a Forex broker. This will allow you to practice trading without risking real money. You can become familiar with the platform and your chosen strategy.
Start with Simple Strategies
As a beginner, starting with simple strategies will help you get a grasp of how Forex trading works. Once you've mastered a simple strategy, you can then move onto more complex strategies.
Follow the Market
Start following economic news releases, understand how they could potentially impact your trades. Always keep track of the market trends.
Have a Trading Plan
A trading plan will help you become disciplined and systematic. Your plan should include your risk tolerance, your profit goal, and methodology among other things.
Manage your emotions
Lastly, don't let your emotions control your trading decisions. It's easy to get caught up in the heat of the moment and make impulsive decisions, but this can often lead to losses. Trade systematically, follow your plan, and always assess your performance.
Final Thoughts
Undoubtedly, in this piece, we're focusing on the most effective forex trading strategies in 2024. Alongside this, WikiFX presents comprehensive rankings on various aspects of forex trading, featuring analyses on the most volatile forex pairs, the top-rated forex brokers of 2024, among others. By following us, you stand to gain enriched knowledge and deeper insight into the world of forex trading. We invite you on this journey of discovery and learning.
Forex Risk Disclaimer
Trading Forex (foreign exchange) carries a high level of risk, and may not be suitable for all investors. Before deciding to trade foreign exchange, you should carefully consider your investment objectives, level of experience, risk appetite, and the possibility of incurring losses. There is a possibility that you may sustain a loss of some or all of your initial investment and therefore you should not invest money that you can not afford to lose. You should be aware of all the risks associated with foreign exchange trading and seek advice from an independent financial advisor if you have any doubts.
You Also Like

Forex Day Trading VS Forex Scalping: Which One to Choose?
Unravel the clash of Forex day trading and scalping - grasp their tactics, track differences, and tailor your trade.

How to Hedge Forex Positions? Some Relevant Strategies to Share.
Dive into Forex hedging strategies - reducing risk, seizing opportunities and securing robust trading profits.

Can I Trade Forex without Stop-Loss? Here Lets’ Discuss
Start Forex trading without stop-loss - understand how it works, explore other options and possible risks.

Forex Market Hours: What is the Best Time to Trade Forex?
Master the clock of Forex trading - optimize profits by knowing the best trading times globally!



























