简体中文
繁體中文
English
Pусский
日本語
ภาษาไทย
Tiếng Việt
Bahasa Indonesia
Español
हिन्दी
Filippiiniläinen
Français
Deutsch
Português
Türkçe
한국어
العربية
Why Does the US Yield Curve Inversion Matter?
Abstract:With US equity markets recently under pressure, financial news media have pointed to movement in the bond market as the key catalyst.
Talking Points
- With US equity markets plunging this week, financial news media has been quick to point out movement in the bond market as the key catalyst.
- Portions of the US Treasury yield curve have inverted, sparking fears that the US economy is heading towards a recession within the next two years.
- Key spreads like the 3m5s and 3m10s have inverted.
See the DailyFX Economic Calendar and see what live coverage for key event risk impacting FX markets is scheduled for next week on the DailyFX Webinar Calendar.
Why Do Investors Look at the Yield Curve?
The yield curve, if it‘s based on AA-rated corporate bonds, German Bunds, or US Treasuries, is a reflection of the relationship between risk and time for debt at various maturities. A “normal” yield curve is one in which shorter-term debt instruments have a lower yield than longer-term debt instruments. Why? Put simply, it’s more difficult to predict events the further out into the future you go; investors need to be compenstated for this additional risk with higher yields. This relationship produces a positive sloping yield curve.
When looking at a government bond yield curve (like Bunds or Treasuries), various assessments about the state of the economy can be made at any point in time. Are short-end rates rising rapidly? This could mean that the Fed is signaling a rate hike is coming soon. Or, that there are funding concerns for the federal government. Have long-end rates dropped sharply? This could mean that growth expectations are falling. Or, it could mean that sovereign credit risk is receding. Context obviously matters.
Does the US Treasury Yield Curve Inversion Matter?
It‘s true that part of the US Treasury yield curve started to invert this week. We’ve seen both 2- and 3-year yields rise above 5-year yields. The “flattening” of the yield curve over the past year, predating this weeks inversion, is rather apparent when comparing the shape of the yield curve today relative to that from last December:
The knee-jerk reaction by many market participants, but mainly financial news media, has been to declare the inversion of the US Treasury yield curve as a harbinger of a forthcoming recession. The stats speak for themselves: yield curve inversions (particularly in the 3m5s and 3m10s spreads) predict recessions (more on this shortly).
While there are certainly good reasons for concern – the US-China trade war, the fading impulse of fiscal stimulus from the Trump tax plan, a housing market that is looking weaker amid higher interes rates – its best to take a step back.
Lets Ask the Professor
Amid all of the talk about the US Treasury yield curve inverting this week, the Duke University finance professor who is the godfather of yield curve analysis (his 1986 dissertation explored the concept of using the yield curve to forecast recessions) gave an interview to NPR (which can be listened to here). Professor Campbell Harvey made a few key points regarding the yield curve inversion which traders should take to heart:
1) The model Harvey used initially looked at the 3-month, 5-year spread (3m5s), and conventional wisdom points to the 2-year, 10-year (2s10s) spread as the yield curve; all of the concern this week about the 2-year, 5-year (2s5s) and 3-year, 5-year (3s5s) spreads inverting did not interest him, given that they as shorter-maturity instruments didnt qualify as “short-term” enough in his model;
US Treasury Yield Curves: 3m5s and 2s10 (1975 to 2018) (Chart 1)
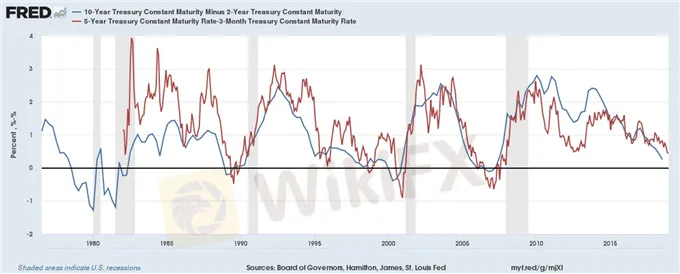
2) The yield curve inversions being discussed now are not significant. According to his research, the yield curve needs to invert for at least one full quarter (or three months) in order to give a true predictive signal (since the 1960s, a full quarter of inversion has predicted every recession correctly);
3) Regardless of the 3m5s and 2s10s curves not inverting this week, Harvey still believes the period of aggressive flattening is significant and it the yield curve is signaling slower economic growth for the US, but not yet a recession.
-
Disclaimer:
The views in this article only represent the author's personal views, and do not constitute investment advice on this platform. This platform does not guarantee the accuracy, completeness and timeliness of the information in the article, and will not be liable for any loss caused by the use of or reliance on the information in the article.
Read more

KVB Market Analysis | 30 August: JPY Strengthens Against USD Amid Strong Q2 GDP and BoJ Rate Hike Speculation
The Japanese Yen (JPY) strengthened against the US Dollar (USD) on Thursday, boosted by stronger-than-expected Q2 GDP growth in Japan, raising hopes for a BoJ rate hike. Despite this, the USD/JPY pair found support from higher US Treasury yields, though gains may be capped by expectations of a Fed rate cut in September.

KVB Market Analysis | 28 August: Yen Strengthens on BoJ Rate Hike Hints; USD/JPY Faces Uncertainty
The Japanese Yen rose 0.7% against the US Dollar after BoJ Governor Kazuo Ueda hinted at potential rate hikes. This coincided with a recovery in Asian markets, aided by stronger Chinese stocks. With the July FOMC minutes already pointing to a September rate cut, the US Dollar might edge higher into the weekend.

KVB Market Analysis | 27 August: AUD/USD Holds Below Seven-Month High Amid Divergent Central Bank Policies
The Australian Dollar (AUD) traded sideways against the US Dollar (USD) on Tuesday, staying just below the seven-month high of 0.6798 reached on Monday. The downside for the AUD/USD pair is expected to be limited due to differing policy outlooks between the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the US Federal Reserve. The RBA Minutes indicated that a rate cut is unlikely soon, and Governor Michele Bullock affirmed the central bank's readiness to raise rates again if necessary to combat inflation.

KVB Market Analysis | 26 August: Bitcoin (BTC) Breaks Out Above $60,000, Faces Resistance at $72,000
Bitcoin traded above $60,000 on Friday, gaining over 4% this week but staying within a $57,000 to $62,000 range for the past 15 days. On-chain data reveals mixed signals, with institutions accumulating while some large holders are selling. Inflows into US spot Bitcoin ETFs and potential volatility from ongoing Mt.Gox fund movements could impact Bitcoin's price in the coming days.
WikiFX Broker
Latest News
PH SEC Issues Crypto Guidelines for Crypto-Asset Service Providers
FTX Chapter 11 Restructuring Plan Activated: $16 Billion to Be Distributed
Think Before You Click: Malaysian Loses RM240,000 to Investment Scam
Share Industry Insights and Discuss Forex Market Trends
Top 9 Financial Fraud Cases in Recent History
KuCoin Pay Introduces Easy Crypto Payments for Merchants
Malaysian Man Killed in Alleged Forex Dispute-Related Attack
How Big is the Impact of the USD-JPY Rate Gap on the Yen?
What Euro Investors Can't Afford to Miss
Is OneRoyal the Right Broker for You?
Currency Calculator






